Rheumatoid Arthritis: Understanding the Chronic Inflammatory Disease
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the joints and other tissues in the body. It is a debilitating disease that can cause significant pain, swelling, and loss of mobility. The causes of RA are still unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
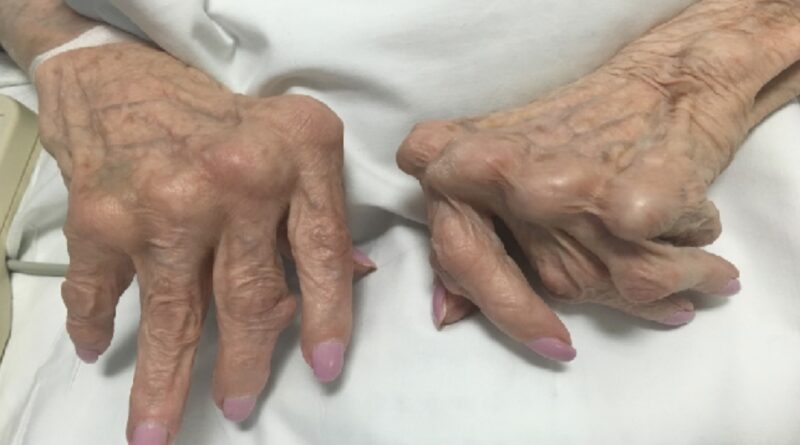
RA is a symmetrical disease, meaning it affects the same joints on both sides of the body. It typically starts in the small joints of the hands and feet and can spread to the wrists, elbows, knees, and ankles. The inflammation caused by RA can damage the cartilage, bone, and other structures in the affected joints, leading to chronic pain, stiffness, and deformity.
The symptoms of RA can vary greatly from person to person and can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
Pain and swelling in the joints
Stiffness, especially in the morning or after sitting for a long period of time
Decreased range of motion and flexibility
Fatigue
Low-grade fever
Loss of appetite and weight loss
Diagnosis of RA is based on a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. Blood tests can help detect the presence of inflammation and antibodies associated with RA. X-rays and other imaging tests can help to evaluate the extent of joint damage.
There is no cure for RA, but it can be managed with a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. The main goals of treatment are to reduce pain and swelling, slow the progression of joint damage, and improve physical function and quality of life.
Medications used to treat RA include:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to relieve pain and reduce inflammation
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to slow the progression of joint damage
Biologic agents, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, to block the action of specific proteins that contribute to inflammation
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes can help manage RA symptoms and improve overall health. Some of these changes include:
Eating a healthy and balanced diet
Maintaining a healthy weight
Engaging in regular physical activity and exercise, such as swimming, yoga, or low-impact aerobics
Avoiding activities that can put stress on the joints, such as heavy lifting or repetitive motions
Getting enough rest and managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises
RA is a chronic condition that can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. However, with proper treatment and lifestyle changes, people with RA can lead active and fulfilling lives. If you have symptoms of RA, it is important to see a doctor for an evaluation and to start the appropriate treatment.